Turmeric for sport recovery
Post-training and sport recovery
When practicing sport, independently of the athletic level, muscle pain can affect anyone. Indeed, intense activity causes muscle damage and triggers inflammatory responses, referred to as exercise-induced muscle damage (EIMD). Their degree depends on the duration, frequency and type of exercise.
It has been described that unfamiliar exercises, muscle contractions and unaccustomed activities during medium or high intensity exercise can induce several symptoms.
Symptoms observed post-workout:
- Pain or discomfort, commonly characterize as delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS)
- Muscle stiffness
- Loss of muscle function and strength, limiting physical function for several days after
- Inability to pursue training programs
- Decreased exercise performance or injuries
Management of sport recovery
In sport medicine, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) are frequently used to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with over-worked muscles. However, while evidence suggests that NSAIDs can improve recovery after acute soft tissue injury, long-term healing can be impaired and adverse events have a significant clinical relevance.
For these reasons, science attempts to replace this pharmacological approach with natural remedies. Nutraceuticals bioactive compounds like polyphenols, catechins and anthocyanins or other nutritional compounds such as proteins, caffeine, omega-3 fatty acids, and amino acids have shown promising results.
Nowadays, curcuminoids from turmeric are increasingly popular as they represent a valuable asset for sport recovery for several reasons:
- powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties
- potential to modulate pathways associated with exercise-induced muscle injury
- an increasing demand for natural, organic, vegan supplements
Over the last decade, the number of sport nutrition products containing turmeric has been multiplied by 7.
What does science say?
Various studies have reported that curcumin and curcuminoids may help reduce muscle damage, and related inflammation, and oxidative stress.
Pre-clinical studies showed several benefits of curcumin and curcuminoids after exercise, such as muscle regeneration.
Meta-analyses of human studies reported that curcuminoid supplementation with standardized turmeric extracts or optimized turmeric formulations at doses up to 6060 mg/day had positive effects before and after exercise: reduced pain, muscle injury and improved muscle function.

Thus, we strongly believe that an acute daily intake of a high dose of curcuminoids (2000-2500mg of PHYT) could alleviate the post-workout symptoms in a short period of time.
And because a cost-effective dose of 300mg of TurmiPure Gold® delivers as many curcuminoids in blood as 2872mg of PHYT, a single capsule of TurmiPure Gold® could provide significant benefits in subjects suffering from muscle stiffness and injury.
TAKE HOME MESSAGES
How does it work? Mechanism of action
Inflammation is a physiological process in response to physical exercise. However, mechanical stress derived from exercise triggers the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), sustaining the inflammation. This process leads to secondary muscle damage and prolonged decreases in muscle strength, muscle function, range of motion (ROM), and increases in blood enzyme activity such as lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatine kinase (CK), myoglobin (Mb), and at a lesser extend transaminases (alanine and aspartate aminotransferases, respectively ALT and AST).
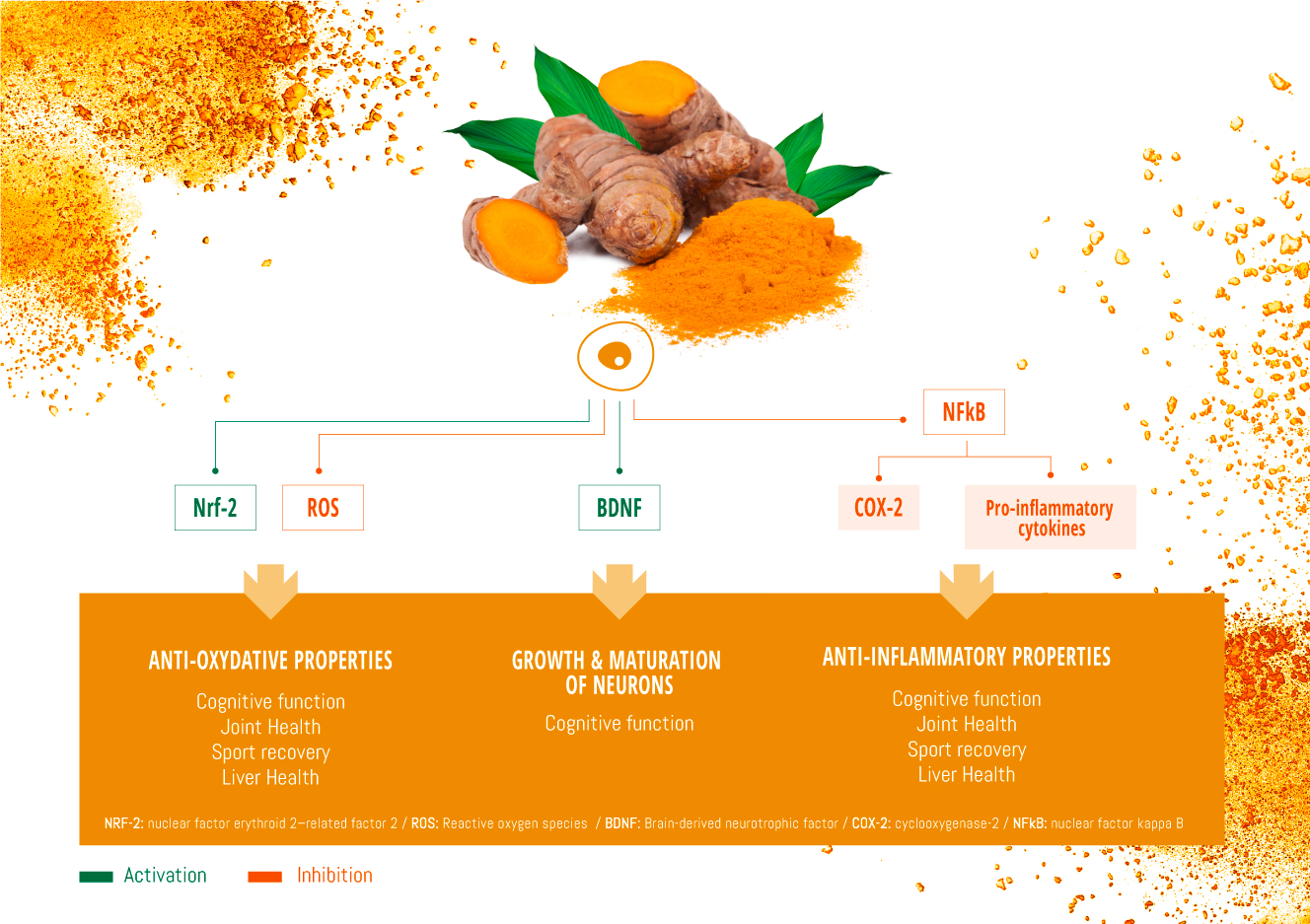
Turmeric has shown an ability to support sport recovery by influencing the following physiological mechanisms:
- Reduction of markers of inflammation and muscle damage
- Reduction of exercise-induced oxidative stress
- Preservation of muscle integrity by fighting free radicals




